“We show that MSK1 retains its importance in converting positive experience into tangible synaptic and cognitive benefits well into old age […]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 25, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 13, entitled, “MSK1 is required for the beneficial synaptic and cognitive effects of enriched experience across the lifespan.”
Positive experiences, such as social interaction, cognitive training and physical exercise, have been shown to ameliorate some of the harms to cognition associated with aging. Animal models of positive interventions, commonly known as environmental enrichment, strongly influence neuronal morphology and synaptic function and enhance cognitive performance. While the profound structural and functional benefits of enrichment have been appreciated for decades, little is known as to how the environment influences neurons to respond and adapt to these positive sensory experiences.
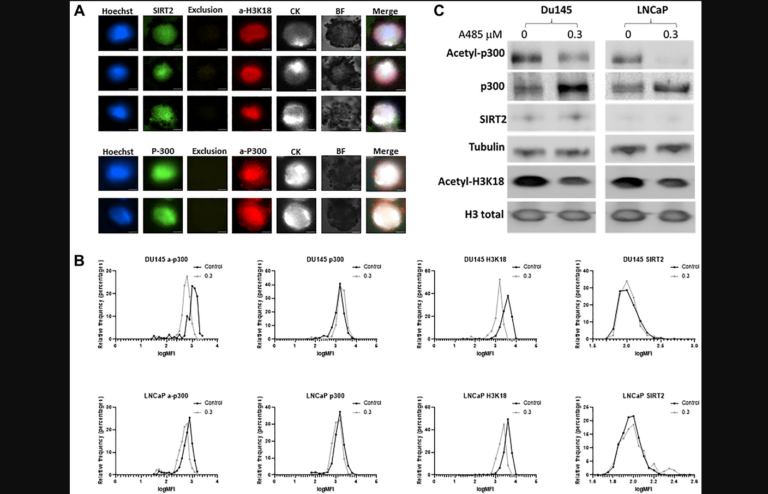
In this new study, researchers Lorenzo Morè, Lucia Privitera, Daniel D. Cooper, Marianthi Tsogka, J. Simon C. Arthur, and Bruno G. Frenguelli from the University of Warwick, University of Central Lancashire and University of Dundee show that adult and aged male wild-type mice that underwent a 10-week environmental enrichment protocol demonstrated improved performance in a variety of behavioral tasks, including those testing spatial working and spatial reference memory, and an enhancement in hippocampal long-term potentiation.
“Recently, a neuronal protein kinase, mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1 (MSK1) has been identified as being a prime effector within the mammalian brain of the beneficial effects of enrichment in the early phase of the lifespan (birth to 4 months) [34–38].”
Aged animals in particular benefitted from enrichment, performing spatial memory tasks at levels similar to healthy adult mice. Many of these benefits, including in gene expression, were absent in mice with a mutation in an enzyme, MSK1, which is activated by BDNF, a growth factor implicated in rodent and human cognition. The researchers conclude that enrichment is beneficial across the lifespan and that MSK1 is required for the full extent of these experience-induced improvements of cognitive abilities, synaptic plasticity and gene expression.
“We show that MSK1 retains its importance in converting positive experience into tangible synaptic and cognitive benefits well into old age, reinforcing the aged brain’s capacity to benefit from positive experience, MSK1’s prominence as a key player in the response to enrichment, and its potential as a target for enviromimetics.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204833
Corresponding Author: Bruno G. Frenguelli
Corresponding Email: b.g.frenguelli@warwick.ac.uk
Keywords: cognitive reserve, synaptic plasticity, anxiety, spatial memory, LTP
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204833
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com