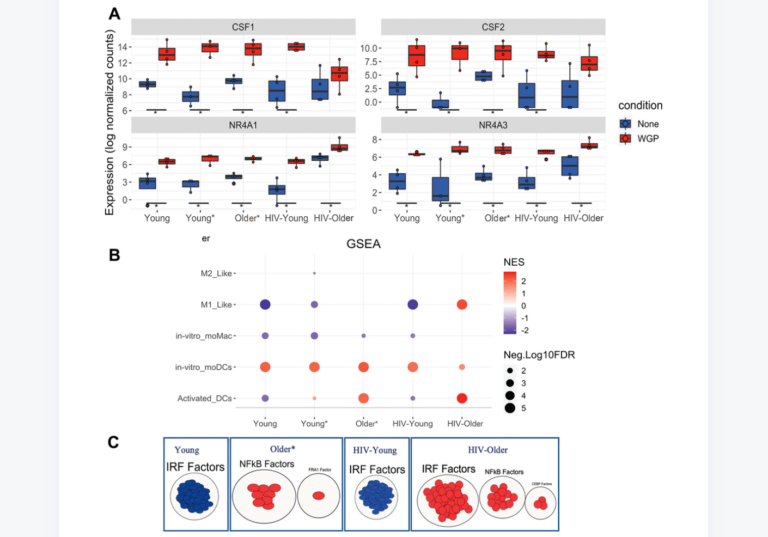
“Overall, our study identified previously unknown circadian transcriptome reorganization of pancreas by aging […]”
BUFFALO, NY- September 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, “Reorganization of pancreas circadian transcriptome with aging.”
The evolutionarily conserved circadian system allows organisms to synchronize internal processes with 24-h cycling environmental timing cues, ensuring optimal adaptation. Like other organs, the pancreas function is under circadian control. Recent evidence suggests that aging by itself is associated with altered circadian homeostasis in different tissues which could affect the organ’s resiliency to aging-related pathologies.
Pancreas pathologies of either endocrine or exocrine components are age-related. Whether pancreas circadian transcriptome output is affected by age is still unknown. In their new study, researchers Deepak Sharma, Caitlin R. Wessel, Mahboobeh Mahdavinia, Fabian Preuss, and Faraz Bishehsari from Rush University and University of Wisconsin-Parkside profiled the impact of age on the pancreatic transcriptome over a full circadian cycle and elucidated a circadian transcriptome reorganization of pancreas by aging.
“Here we carried out a 24-h circadian transcriptomic analysis of pancreas from male mice at young and old ages.”
The researchers defined a comprehensive circadian transcriptome landscape and identified biological pathways that are reflective of aging pancreas. Additionally, analysis of the pancreatic microenvironment revealed novel mechanistic insights into the fibroblast-mediated regulation of rhythmicity in aged pancreas. The team suggests that the circadian transcriptome in aging pancreas re-organizes in response to age-specific signals from the cellular microenvironment, primarily modulated by fibroblasts.
“Our study highlights gain of rhythms in the extrinsic cellular pathways in the aged pancreas and extends a potential role to fibroblast-associated mechanisms.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204929
Corresponding Author: Faraz Bishehsari
Corresponding Email: Faraz_Bishehsari@rush.edu
Keywords: circadian rhythms, aging, RNA transcriptomics, pancreas
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204929
About Aging: Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.